|
|
User manual for the Ferro Backup System™ 6
for administrators and operators of backups
- FBS Server (Server) - Introduction
- Backup - planning and supervising backup tasks
- Workstation settings
- Advanced
- Remote commands - scripts to be executed on workstations
- Backup task settings
- Schedule - backup filing schedule
- Range - selection of files and directories for backup
- Options - selection of archiving, encryption types
- Task replication
- Replication - duplicating backup
- Disk drives - NAS, external hard drive, FTP server
- Optical drives - CD, DVD, HD-DVD, Blu-Ray
- Tape drives - DDS, DLT, LTO
- Restore - restore of archived data
- Network monitor - supervising the operation of the TCP server
- Event Log - list of errors, warnings and information
- Reports - reports and statistics
- Backup server settings
- Basic - database, encryption, updates
- Users - blocked access to control console
- Administrative alerts - e-mail notifications
- Network resources - hard drive and network share mapping
- Local scripts - scripts to be executed on backup server
- Passwords - encryption and decryption passwords for archives
- Startup - startup methods
- Program startup in the system service mode
- Program startup in the diagnostics mode
- Solving control console access problems
- Syntax and command shell parameters
- FBS Worker (Client) - Introduction
- Description of available configuration file options
- Launching and stopping
- Syntax and command shell parameters
- Solving connection problems
User manual for the Ferro Backup System™ - Introduction
FBS Server is the main application within the Ferro Backup System. It is activated only on one computer in the network, which will function as backup server. It is used to prepare and send backup tasks as well as receive and save backups. The application console includes seven main tabs which allow the whole System (server and workstations) to be monitored, to configure it, check on scheduled tasks and restore data. All tabs and dialogs are described in the following chapters.
Access to control console
FBS Server program runs in the background, as a system service. Access to control console by HTTP protocol on 4530 port. In order to connect the control console, open the Internet browser and type name or IP address of the backup server, i.e. the computer on which FBS Server runs, and 4530 port, e.g.:
http://127.0.0.1:4530/
http://localhost:4530/
If the Internet browser cannot display the page, read: Solving control console access problems
Table sorting
- Click on the heading of the column according to which you want to sort the table
- To reverse sorting order, click the column heading again
- To sort the table according to multiple columns, select their headings one by one while holding down SHIFT
- To disable sorting, click the column heading while holding down CTRL
- If after clicking on the column heading an arrow indicating the sorting order does not appear, it means that sorting is unavailable for that column
Table filtering
- Move the pointer over the column heading and click on the displayed filter button.
- To add a new filtering rule or modify an existing filter, click on Apply in the lower right corner of the table
- To turn off filtering, click on X in the lower-left corner of the table
- If the filter button does not appear when you move the pointer over a column heading, it means that filtering is unavailable for that column
1. FBS Server - Backup
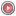
The Backup tab is used to track the activities of workstations (active/inactive/task running), define new workstations in the System, change workstation settings and remove workstations from the System. The information window includes three views: Stations and Tasks, Stations, Tasks. Stations and Tasks tab includes tree display of the most important information on workstations and their backup tasks. The Stations tab displays detailed information about particular workstations. The Tasks tab displays a detailed list of all scheduled backup tasks. In all views the following information is displayed in columns:
- Station status - current status of workstation:
 No connection No connection
 Ready to work Ready to work
 Task preparation on server side Task preparation on server side
 Task running Task running
 Software update Software update
 Workstation disabled Workstation disabled
- Task status - Current backup task status:
 Stopped Stopped
 Running Running
- Workstation/task name - workstation or backup task name
- Last time - date and time of last backup
- Delta time - time remaining until task execution (-), task duration (+) or task delay (+ red)
- Next backup - date and time of next backup
- Last event - last message on the workstation or backup task
- Description- any text describing the workstation or backup task
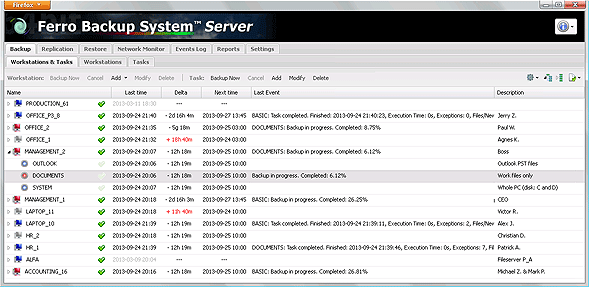
Fig. 1.1 FBS Server - Backup
Description of available commands (when one or more workstations selected):
- Backup now - performs default backup task on the selected workstations.
- Cancel - cancels the current backup task on the selected workstations.
- Add - adds a new workstation with default settings.
- Add all non-configured stations - adds all connected workstations, which are not yet added.
- Modify - displays a configuration window for adjusting the settings of the selected workstations.
- Delete - deletes selected workstations and their backup tasks.
Description of available commands (when one or more backup tasks selected):
- Backup now - starts selected backup task.
- Cancel - cancels selected backup tasks.
- Add - displays a configuration window for defining all parameters of a new backup task. New task will be added to all workstations, the existing tasks of which have been selected.
- Modify - displays a configuration window for modifying the settings of the selected backup tasks
- Delete - deletes the selected backup tasks. For every workstation there has to be at least one (default) backup task. A default task cannot be deleted. In order to delete all the tasks of the workstation, select and delete the entire workstation.
Multiediting - global settings editing
After selecting several workstations or backup tasks (SHIFT + Click, CTRL + Click), the type Setting window works in the global settings editing mode. In this mode, the multiediting menu, which helps define the modification mode, fields to save, is available in the lower part of the window. This way, it is possible to quickly change one or multiple settings for all selected workstations and tasks.
Input settings are read from the benchmark position. The benchmark position is the first selected workstation or backup task from the top. The name of the benchmark station or task is displayed as first on the settings window title bar.
To change the benchmark position after selecting a workstation group or backup task group, click the selected workstation or backup task while holding CTRL.
1A) Changing workstation settings
The Workstation Settings window is used to add or modify settings for selected workstations (of a remote computer) or the selected workstation group. The most frequent changes include: workstation description, compression level, blocked files backup and remote commands. The window appears after clicking Add or Modify in the main window in the Backup tab. See below for a detailed overview of all the settings available in this window.
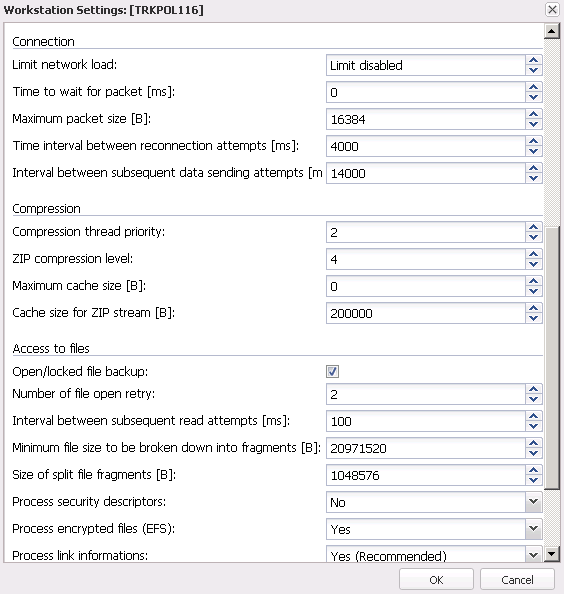
Fig. 1.2 FBS Server - Workstation Settings window
General
- Active workstation - turns the workstation on or off. If the workstation is not active, the server does not plan any backup tasks for it and does not warn about pending tasks.
- Friendly name - any text facilitating computer identification, e.g. file server or accountant.
- Group name - any text defining a group of computers, e.g. servers or accounting.
- Computer description - space for comments regarding the workstation.
Advanced
 WARNING. Changing the advanced settings is not necessary to ensure proper operation of the software. Changing some parameters may disrupt data transmission or prevent the workstation from reestablishing the connection. WARNING. Changing the advanced settings is not necessary to ensure proper operation of the software. Changing some parameters may disrupt data transmission or prevent the workstation from reestablishing the connection.
Connection
- Limit network load - defines a given workstation's maximum network load. See also: Limit connection speed for all workstations
- Maximum data transfer rate
- Unit: kilobit/sec. [kb/s]
- Range: 50 - 1 000 000
- Default value: 4 000 (= 4 Mb/s)
- From/Until - defines the time interval in which the restriction is active
- Except - defines an exception or a situation when the restriction is not active
- Saturdays and Sundays
- Sundays
- If the connection comes from an IP address - specifies the IP address, several IP addresses or network masks to restrict. Individual addresses or network masks are separated by commas.
In the network mask, the * (asterisk) character can be used as a wildcard. By providing a - (minus) sign before the IP address or network mask, the limitation can be reversed. Examples:
- 10.1.2.100,10.1.2.101 - the limit will be active if the remote computer connects from the IP address 10.1.2.100 or 10.1.2.101
- 10.1.2. * - the limit will be active if the remote computer connects from any IP address in the range from 10.1.2.1 to 10.1.2.254
- 10.1.2. *, - 10.1.2.200 - the limit will be active if the remote computer connects from any IP address in the range from 10.1.2.1 to 10.1.2.254 excluding the address 10.1.2.200
- -192.168. *. * - the limit will be active when the remote computer connects from any IP address, excluding the IP addresses 192.168. *. *
- Time to wait for packet - Time to wait for a packet. Currently this needs to be set to 0.
- Unit: milliseconds [ms]
- Range: 0 (no time limits) - 16777216
- Default value: 0
- Maximum packet size - Maximum size of transmitted packets. Entering a value higher than 16384 can increase the transfer rate but if the transmission is broken while the backup is being sent the received file may contain errors (packets lost).
- Unit: bytes [B]
- Range: 512 - 16777216
- Default value: 16384
- Time interval between reconnection attempts - Time interval between subsequent attempts to reconnect to the server.
- Unit: milliseconds [ms]
- Range: 0 (immediate) - 16777216
- Default value: 4000
- Interval between subsequent data sending attempts - Time interval between subsequent attempts to send data
- Unit: milliseconds [ms]
- Range: 0 (no delay) - 16777216
- Default value: 14000
Compression
- Compression priority - defines maximum CPU usage during backup. During a backup operation FBS Worker reads files from a disk, compresses them and sends them to the server. This places a significant load on the CPU, particularly using poor equipment. If the backup is performed while the user keeps working with the computer, it is possible, for comfort, to set a lower compression priority. 0 means the lowest and 6 the highest priority. To ensure user comfort, you can set it to 0, meaning the application will only compress when the CPU is idle. Setting it to anything below default value will involve less CPU usage and longer backup times. Setting it higher than default value may shorten backup times.
 Note. Setting the priority to 6 may mean that the operating system will not respond to the user's commands until the backup is completed. Note. Setting the priority to 6 may mean that the operating system will not respond to the user's commands until the backup is completed.
- Range: 0 - Idle, 1 - Lowest, 2 - Lower, 3 - Normal, 4 - Higher, 5 - Highest, 6 - Time Critical
- Default value: 2
- ZIP compression level - ZIP compression level. Range: 0 (no compression), 1-3 (fast compression), 4-6 (standard compression), 7-9 (maximum compression). Default value: 4 0 means that the files will not be compressed. Values between 1 and 9 define compression level. Small values mean faster compression, less CPU usage and larger archives. High values mean better compression (smaller archives), longer compression times, more CPU and memory usage.
- Maximum cache - Maximum buffer used for file compression. If set to 0, the best buffer size will be used - ranging between 524288 and 1572864 B. If small values are used (less than the default) compression times are longer and the resulting ZIP archives are larger (lower compression). It is not recommended to use high values (higher than the default). This will consume more memory, lengthen compression times and only slightly improve compression.
- Unit: bytes [B]
- Range: 0 (default size), 512 - 16777216
- Default value: 0
- Cache size for ZIP stream - The size of the cache memory for the compressed ZIP stream. 0 means switching off cache memory. The upper value is limited by the size of the available RAM. In order to limit demand on the application's memory, you can reduce the cache below the default value. However, if the cache is set below 65536 B, transmission speeds fall dramatically, the amount of information sent over the network rises sharply and the load on the workstation's and the backup server's CPU increases. Values higher than the default may increase the backup speed, reduce the amount of data sent over the network and reduce the load on the workstation's and the backup server's CPU. If the set cache value is higher than the available RAM, backup will not be possible (error: out of memory).
- bytes [B]
- Range: 0 - 1073741824
- Default value: 200000
Access to files
- Open/locked file backup - (Open File Manager) this can be used to backup open files, i.e. files which are locked by other processes in the system. Files are backed up in the OFM only if they cannot be opened any other way. Most often locked files are database files and system files. For large files (> 100 MB) it is recommended to schedule backups for periods when information is saved less frequently. If the OFM cannot obtain a coherent file image within 60 seconds (for database files this is the status after a transaction), the file will be skipped and a relevant note made in the Event Log.
 Note. Files which are open (locked exclusively) can only be backed up under: Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows 2003, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 2008, Windows 8, Windows 2012. Files need to be placed on a local, uncompressed FAT 12, FAT 16, FAT 32 or NTFS partition. Note. Files which are open (locked exclusively) can only be backed up under: Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows 2003, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 2008, Windows 8, Windows 2012. Files need to be placed on a local, uncompressed FAT 12, FAT 16, FAT 32 or NTFS partition.
- File open retry - Number of attempts to open a file. This is used to define how many times the application should retry to open an input file if a read error is encountered. If during the backup operation there are errors caused by the application's inability to ensure the integrity of input files, this should be set to a higher value.
- Range: 0 (no retries) - 255
- Default value: 2
- Interval between subsequent read attempts - The interval between subsequent read attempts of source files. This defines the time interval between subsequent attempts to read a source file. Set this value higher if there are integrity errors in input files.
- Range: 0 (immediate) - 65535
- Default value: 2
- Unit: milliseconds [ms]
- Minimum file size to be broken down into fragments - sets the file size threshold - if this is exceeded, differential backups will be performed on the file fragment level. See also: Backup type - file fragment difference
See also: Backup type - file fragment difference
- Range: 102400 - 2146435072
- Default: 20971520 (20 MB)
- Unit: byte [B]
- Size of split file fragments – sets the size of fragments which the backed up file will be split into (virtually).
Values lower than the default can save disk space on the backup server and speed up the backup process.
The default value has been calculated for 1 GB files.
If file(s) larger than that are backed up, setting this value lower may increase backup verification time and slow down backup preparation.
If the file size exceeds 10 GB, increasing the value of this parameter can speed up the recovery process. For files larger than 50 GB, the minimum recommended value is 10485760 (10 MB).
See also: Backup type - file fragment difference
- Range: 131072 - 2054275072
- Default: 1048576 (1 MB)
- Unit: byte [B]
- Process security descriptors - defines whether to save information on file and directory authorizations. This option may be useful for file servers in order not to redefine access privileges after file recovery. Turn off this option if saving security descriptors is not necessary. Turning this option off increases backup size, RAM use by program and slows down the backup process.
- No (default value) - does not save information on security
- DACL - saves the Discretionary Access Control List together with files and directories
- SACL - saves the System Access Control List together with files and directories
- DACL+SACL - saves both access control lists together with files and directories
See also: Restoring security descriptors
- Process encrypted files (EFS) - defines whether to process encrypted files on NTFS partitions. Encrypted files are backed up encrypted and can be restored only on NTFS partition.
- Yes (default value) - backs up encrypted files
- No - skips encrypted files and reports warnings "Access denied"
 WARNING. EFS certificates and keys are required to decrypt files after restoring them on another computer. Remember to make a backup copy of certificates and EFS keys or a system register, in which they are stored. Otherwise, it will not be possible to decrypt the restored files.
WARNING. EFS certificates and keys are required to decrypt files after restoring them on another computer. Remember to make a backup copy of certificates and EFS keys or a system register, in which they are stored. Otherwise, it will not be possible to decrypt the restored files.
- Process link information - defines whether after a link (Reparse Point, Junction Point, Symbolic Link) it is necessary to process elements in the target point or to store only information on the link.
- Yes (Default value) - saves information about the link
- No (Not recommended) - process links as target objects
 WARNING. Following hook ups is not recommended because the same files may be backed up more than once, which may lead to recursive looping.
WARNING. Following hook ups is not recommended because the same files may be backed up more than once, which may lead to recursive looping.
Other
- Synchronize workstation clock with server - if this field is active, the date and time on the workstation will be synced with the date and time on the server. Synchronization takes place whenever a connection is established and whenever time or date settings are changed on the workstation.
- Generate warnings on network errors - if this field is active, the program will generate warnings if network errors occur (disconnection and reconnection of the workstation). If the workstation uses radio access network, this option can be turned off.
- Allow user to cancel backup - if this option is active, the user may cancel the backup and shut down the computer immediately. (This option is global for all of a given workstation's backup tasks. If this option is changed in one task, it will change in all other tasks.)
- Associate the workstation with this backup server - this option allows to block network connections with unauthenticated backup servers by associating (pairing) the workstation with a specific backup server.
When installing the client (FBS Worker), the network name or IP address of our backup server is defined. The client automatically connects to the specified backup server. If a workstation is connected to another computer network, where there is a foreign backup server with the same IP address or network name, the workstation will connect to this computer. This option must be enabled to make the workstation connect only with our backup server. To enable the connection of a workstation to another backup server, this option must be disabled or the client's software must be uninstalled and reinstalled on the workstation.
Remote Commands
Remote commands are plugins and they expand functionalities of FBS Worker - the client's software. They can be used to run additional commands, scripts or applications on workstations. For example: before backup you can map a network drive or stop a database server, and after backup you can defragment a drive or shut down the system.
Remote commands are launched with the privileges of the account, on which FBS Worker runs.
The available options are as follows:
- Add - adds a new remote command
- Delete - deletes a selected remote command
- Test - sends a remote command to the workstation and launches it. The result of a remote command will be returned to the control console.
- Launch - allows to specify when the remote command is supposed to be launched. The following types are available:
- When starting the application (FBS Worker)
- Before backup
- After backup
- Wait - here you can choose whether FBS Worker, after launching a remote command, should wait for its completion before continuing with the task or not. This option should be active if a backup task or other remote commands depend on the result of the remote command (see: example no. 2).
- Command - defines the name of an executable file (.exe, .bat, .cmd, etc.). If necessary, enter the full path before the file name.
- Parameters - (optional) list of parameters to be sent to the executable file when it is launched. You can use Windows environment variables (local variables and system variables) (e.g.. %COMPUTERNAME%, %USERNAME%) and software variables %TASKNAME%. The %TASKNAME% variable will be replaced with the name of the current backup task when the command is launched (e.g. BASIC). The use of the %TASKNAME% variable enables you to execute a remote command on a contingent basis, depending on the backup task in progress.
Example 1 - passing %TASKNAME% variable value to a batch file as %1 parameter
Command: C:\example.bat
Parameters: %TASKNAME%
Example 2 - conditional execution of "defrag C:" command
Command: CMD
Parameters: /C if %TASKNAME% == BASIC defrag C:
See also:
1B) Changing backup task settings
The Task Settings window is used to add or modify settings for a backup task or group of tasks. The most often changed settings include: task name, schedule, range, backup type and versioning. The window appears after clicking Add or Modify in the main window in the Backup tab. See below for a detailed overview of all the settings available in this window.
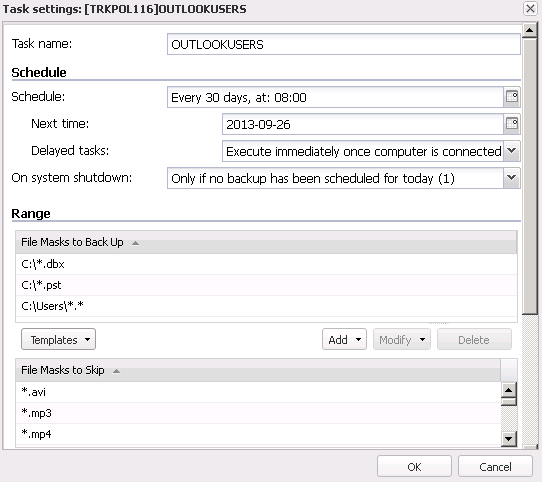
Fig. 1.2 FBS Server - Workstation Settings - Tasks/Schedule
General
- Task name - defines the back up task name. The most frequently used are names that describe backup range or frequency, e.g.: DOCUMENTS_EVERYDAY, SYSTEM_FRIDAY.
- Default task - a task marked as "Default" is run when the workstation is active and the button "Back up now" is pressed in the application's main window.
Schedule - scheduling backup tasks.
You can in the first available field select the schedule type. The following types are available:
- On demand - The backup operation will only be run by manually launching the task in the application's main window (button: Back up now)
- Daily - The backup task will be run every day at the time indicated in the field Start time.
- Day Intervals - The backup task will be run automatically after a certain number of days.
- Hour Intervals - The backup task will be run automatically after a certain number of hours.
- Minute Intervals - The backup task will be run automatically after a certain number of minutes.
- Days of the week - The backup task will be run automatically on selected days of the week as defined in the Days of the Week field.
- Start Time - In the Start Time field you can schedule the archive task start time to 1 minute.
- Next Time - In the Next Time field you can set the date for the next backup operation.
- Delayed tasks
- Skip and execute later- the task will only be executed at a specified Start Time. If the workstation is not connected to the server at this specified time, the task will not be executed until the next time.
- Execute immediately once computer is connected - if the workstation was unavailable at the specified time, the task will be executed immediately upon connecting the workstation to the server. This option is recommended for laptops as they are often unavailable at a specified time.
- Warn of delays longer than [times] – if a task has not been completed the selected number of times, a delay warning entry will be made in the Event Log.
- Backup on system shutdown - you can choose whether file backup should be done before shutting down the computer.
- Turn off - do not activate backup on system shutdown
- Only when the backup scheduled for today has not yet been made (1) - the backup will be performed before shutting down the system only if a backup operation has been scheduled for the current day. This option enables you to execute a backup operation scheduled for a given day even if the user shuts the computer down before the scheduled backup start time. After the backup is completed using this option, a new backup is scheduled based on the predefined schedule. The option is not available if the schedule is turned off (On demand only)
Example:
-Schedule: Daily, 5 pm, Back up before system shutdown: YES
-Next time: 2007-08-20 17:00:00
-The system is shut down at 3:30 pm. The task is launched. After the task is completed, the next backup is scheduled for: 2007-08-21 17:00:00
- Always (2) - a backup will be performed at each system shutdown. Unlike the previous option, the backup schedule with the "always" option on is not updated after the backup is completed (no new backup is scheduled).
Disk failures most often occur during power on or off. The "Backup before system shutdown" option has been added in order to enhance data protection. It backs up all files created or modified since the last backup, even when the user shuts down the computer prior to the scheduled periodical backup.
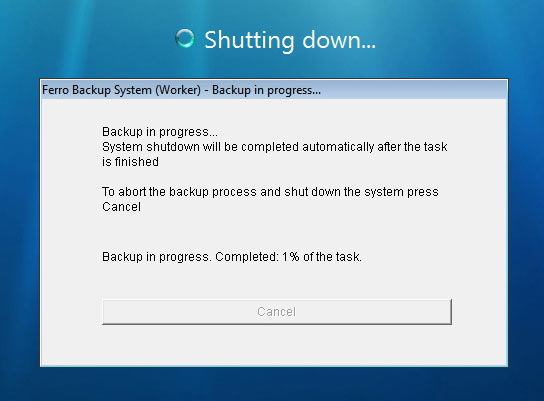
Fig. 1.3 FBS Worker - the information window displayed during system shutdown
If this option is on, the backup is started when the user attempts to shut down the system (selecting "shut down" or pressing the power button on the computer). A dialog appears informing the user that the backup operation has started. The workstation user may cancel the backup and shut down the system immediately by pressing the Cancel button.
If this option is active and the user shuts down the computer during the backup process (launched according to the schedule or manually by the administrator), this task is continued as if it has been launched by the system shut down event; if this option is disabled, the backup task will be aborted.
 Note. If the "Back up before system shutdown" option is on, the dialog may be displayed for a certain time (~10 seconds) at each system shutdown, even if no backup is required according to the current settings. During that time FBS Worker will interface with the FBS Server to check whether the task needs to be launched.
Note. If the "Back up before system shutdown" option is on, the dialog may be displayed for a certain time (~10 seconds) at each system shutdown, even if no backup is required according to the current settings. During that time FBS Worker will interface with the FBS Server to check whether the task needs to be launched.
The system shutdown will be completed after the backup operation is finished or connection with the backup server is lost.
Range - here you can select files and directories for backup
In the Range part, you can define volumes, masks or full paths to files and directories, for which backup is going to be executed and those, which are going to be excluded from backup. After clicking Add or Modify, a dialog is displayed, which contains a list of drives, directories and files of the remote computer.
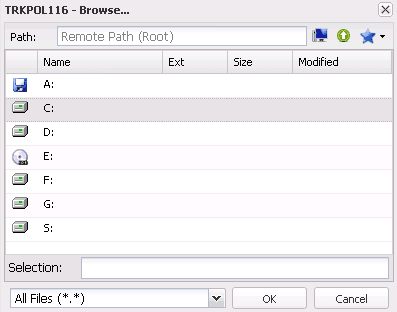
Fig. 1.4 FBS Server - Viewing remote computer resources
- Files and directories for backup - a list of files and directories for backup. The list can include specific files or file masks.
- File Masks to Skip - a list of files and directories to be omitted from the backup operation. The field is used to exclude a file or a number of files from the File Masks to Back up list. The list can include specific files or file masks. See below for a list of files and directories to be excluded from backup. Files and directories from the list are not important to restore. If the backup includes the following files and directories, the backup process may be significantly prolonged. In some situations, backing up these files and directories may make it difficult to complete the task.
- *\Temp\*
- *\Temporary Internet Files\*
 Note. If you intend to back up the whole hard disk, remember to skip the abovementioned files and directories. Note. If you intend to back up the whole hard disk, remember to skip the abovementioned files and directories.
- Add - adds files or file masks to a list (back up list or skip list).
- Modify - enables to change the highlighted file or mask.
- Delete - deletes selected entries from a list.
Examples of the use of in the Files/directories to back up and Files/directories to skip fields:
|
Files backed up
|
Skipped files
|
Overview
|
|
C:\*.*
|
-N/A-
|
All files from C: and all subdirectories will be backed up.
|
C:\*.doc
C:\*.rtf
|
-N/A-
|
All DOC and RTF files from C: and all subdirectories will be backed up.
|
|
C:\*.*
|
C:\Windows\*.*
|
All files from C: and and all subdirectories will be backed up except for files from C:\Windows\ and its subdirectories
|
*.*
|
*\temp\*.*
*\temporary internet files\*.*
|
All files from all local hard disks will be backed up except for files from “temp” and “temporary internet files”
|
Remarks on network drives mapping
In order to back up files located on another computer on which you cannot install FBS Worker and perform the backup operation locally, you need to map the resources of the remote computer under a local drive letter. Please note that the mapped drives visible to the logged user are not available (not visible) to FBS Worker. That is why the drives need to be mapped directly in Ferro Backup System using Remote command (command: NET USE).
Direct access to network resources
The application also allows you to back up the shared resources of another computer without previously mapping it under a local drive letter. In this situation the resources on the remote computer must be available without authentication because there is no way to enter the user name and password. To display a list of files and folders available on the other computer, enter the following path to the UNC in the Path field, in the View window: \\server_name\share_name\ and press ENTER.
 Note. ACCESS TO NETWORK RESOURCES - A local system account on which the FBSWorker is installed by default does not have access privileges to network resources. Therefore it is necessary to switch the FBSWorker service to an account which has such privileges (e.g. an administrator account) or to set relevant privileges for the Local system account. This can be done from the MMC Services console (Control panel->Administrative tools->Services). Note. ACCESS TO NETWORK RESOURCES - A local system account on which the FBSWorker is installed by default does not have access privileges to network resources. Therefore it is necessary to switch the FBSWorker service to an account which has such privileges (e.g. an administrator account) or to set relevant privileges for the Local system account. This can be done from the MMC Services console (Control panel->Administrative tools->Services).
See also:
Options - setting backup task properties
- Backup type
- Full - backup
- Differential - backup. It is recommended in most cases due
to greater speed and space savings on the backup server compared to full backup.
- Delta - .
An advanced option of the differential backup recommended for tasks including files larger than 20 MB which are often modified (mail files, databases, etc.).
- Periodical full backup – this enables you to reduce the level of dependency between differential backup archives.
In the case of differential backups the application only backs up those files which do not exist (or exist only in older versions) in the previous backup files.
Thus after a certain time dependency develops between backup archives – newer archives which are connected with older ones.
When information is restored from a differential copy, files are extracted from the selected differential backup archive and previous archives linked to it.
If a large number of archives is stored (see: Rotation copies) and any of the differential backups is damaged
or deleted, some of the files may not be recoverable. To reduce that risk, check this option.
 Note. This option is not required to ensure correct backup and restore.
Note. This option is not required to ensure correct backup and restore.
The period is calculated differently for various backup schedules. Two solutions are used: one based on the quantity of files (ZIP archives),
and the other based on the quantity of scheduled dates. The first one is used for schedules where it is not important when (on what day) the full backup copy will be made.
The other allows specifying the exact date and time of performing a full backup. See the table below for an overview of the Period option functionality along with examples.
|
Backup schedule setting
|
Full backup period calculation
|
- Only on demand
- Daily
- Once in a specified number of days
|
The period is determined based on the number of differential backup copies. In this case, a full backup will be executed once per given number of differential copies.
Example (F = full; d = differential):
- Period = 2; F/d/F/d/...
- Period = 3; F/d/d/F/d/d/...
|
- Once per given number of hours
- On weekdays
|
The period is determined based on the scheduled dates. In this case, a full backup will be performed once per given number of scheduled dates.
If backup cannot be performed on the scheduled date when the full backup falls (e.g. the computer is unavailable),
full backup will be scheduled for another date as per the scheduled period.
The field Period Start defines the date from which a period runs. Example:
-Schedule: On weekdays = Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri; Period = 5; Period Start = Fri; Full backup performed every Friday
-Schedule: On weekdays = Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat; Period = 3; Period Start = Wed; Full backup performed every Wednesday and Saturday
-Schedule: On weekdays = Mon Wed Fri; Period = 6; Period Start = Fri; Full backup performed every other Friday
-Schedule: Once per given number of hours = 2; Period = 4; Period Start = 1.00 p.m.; Full backup performed once every 8 hours - at 1.00 p.m., 9.00 p.m., 5.00 a.m.
|
- File encryption algorithm – here you can select an algorithm for file encryption.
Three encryption algorithms, currently considered the best, are available: Rijndael, Serpent, Twofish. Just as during compression, encryption is performed on the computer on which the backed up files are located. Thus the backup copies are already secured when they are sent to the over the network. All of the implemented encryption algorithms use 256-bit keys.
The encryption password must be set in the Password management window.
 Note. Encryption may significantly slow down the backup process (Twofish is the fastest encryption, Serpent the slowest).
Please note that ZIP archives encrypted in the Ferro Backup System can only be opened with FBS Server - Restore tab. Note. Encryption may significantly slow down the backup process (Twofish is the fastest encryption, Serpent the slowest).
Please note that ZIP archives encrypted in the Ferro Backup System can only be opened with FBS Server - Restore tab.
- Rotation backups (how many previous copies should be stored) – defines how many backup copies can be stored on the disk. If this option is on, the application will delete the oldest backup file (ZIP file) from the disk if the current number of backup files in the is higher than the value set in this field.
E.g. if the value is 7, after the 8th copy is completed the application will delete the oldest ZIP file.
For differential backups, the last differential backup is deleted.
The option “Optimize to save disk space” applies to differential backups. If it is on, the application will move files between different ZIP archives so that a ZIP file can be deleted as soon as possible, thus freeing up disk space.
 Note. Ferro Backup System uses advanced mechanisms to move files between ZIP files without actually unpacking and repacking (decrypting and encrypting) them again, which significantly speeds up the operation. This should not, however, be used on slower backup servers since the time to complete a backup task may then be significantly longer. Note. Ferro Backup System uses advanced mechanisms to move files between ZIP files without actually unpacking and repacking (decrypting and encrypting) them again, which significantly speeds up the operation. This should not, however, be used on slower backup servers since the time to complete a backup task may then be significantly longer.
- Backup Location - can be defined by an alternative, in relation to the Main Backup Location, backup storage path for the selected backup task
- At backup server (default) - local storage on the backup server. A workstation send its backups to the backup server, and then the FBS Server saves them in a chosen location.
- At workstation - local storage on the workstation. To save backups directly by the FBS Worker on the indicated drive available from the workstation. This option may be used, e.g. for backups of computers outside the company's HQ, where the backup server is located.
Thus, during backup the data do not have to be sent, usually by a low bandwidth, to the backup server.
 In order to ensure the necessary level of efficiency, the backup directory should be located on a local hard disk or an internal disk array (RAID). Using network disks is not recommended. A network disk can be used as an additional storage location. For details see:Replication. In order to ensure the necessary level of efficiency, the backup directory should be located on a local hard disk or an internal disk array (RAID). Using network disks is not recommended. A network disk can be used as an additional storage location. For details see:Replication.
- Comment – here a comment can be added to a backup task
Task replication
Here you can define if the backups that belong to the selected backup task should be copied into another location. Replication may be executed on hard drives, optical drives and streamers. For each type of drive, the following options are available:
- Turn off - the replication will not be executed
- All backup files - all backup files that belong to the given back task will be replicated
- Only full backups - only full backup files that belong to the given back task will be replicated
See also: Replication tab
2. FBS Server - Replication
Replication enhances the security of backup files stored on the by replicating them to another location.
Files can be replicated to another disk drive (removable hard drive, disk array, network drive, NAS, FTP server), optical media (CD/DVD/Blu-Ray/HD-DVD) or tape media (QIC, 4mm DAT/DDS, 8mm, DLT, etc.).
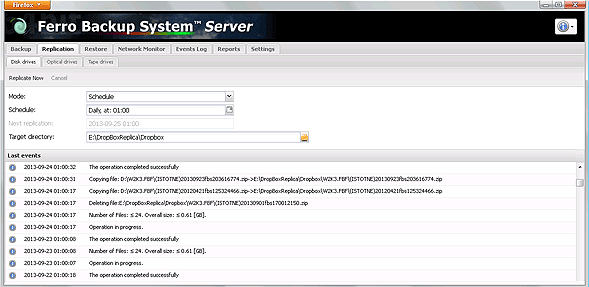
Fig. 2.1 FBS Server - Replication
The Replication tab is divided into three separate subtabs: Disk drives, Optical drives and Tape drives. In each one you can configure replication settings for the selected media. Replication options, which are the same for all drive types, are described below. Drive-specific options are described further on.
All Replication drive types
- Replication (Replication mode):
- Automatic - the replication will be performed automatically when backup and verification operations are completed.
- Schedule - the replication will be performed according to a schedule defined by the administrator
- Manual - the replication will be performed on demand only (Replicate now button)
- Set Schedule - here the user can schedule replications. Replications can be performed at a preset time based on one of the following patterns: daily, every number of days, every number of hours, on selected days of the week. This option is only active when the replication mode is set to "Schedule".
- Replicate now - this will replicate all backups included in backup tasks selected for replication. This is only active when the replication mode is set to "Manual".
- Simulation Mode - this will check that the replication settings are correct and the drives are ready. This command will perform all activities involved in the replication of backups except the actual copying, deleting, writing and marking replicated backups.
- Cancel - use this to stop the current replication process. As writing must be successfully completed, it may take up to several minutes to cancel a replication to optical media or tape media.
- Next replication - here the user can choose the next scheduled time of replication. This option is only active when the replication mode is set to "Schedule".
- Events - an extract from the Event Log describing replication events for the selected drive type.
Replication for the backup task is activated in the Task Settings window, in the Replication section.
Disk drives (external hard drive, network drive, remote share, FTP server etc.)
Backup files on the will be synced with files from the location specified in the field “Target replication directory." in the replication location will be created automatically.
Replication to disk drives involves the synchronization of those backups from the FBF folder which belong to a selected backup task located on the backup server with a folder of the same name stored in the location selected as the "Target (replication) directory".
Backups stored on the backup server which are not in the replication folder will be copied to the replication folder.
Backups in the replication folder which are not on the backup server will be removed from the replication folder.
Archives whose contents on the backup server differs from backups of the same name located in the replication folder will be deleted from the replication folder and copied again.
After the replication of backups assigned to a selected backup task is complete, the backups stored on the backup server and in the replication folder will match.
See also: Using NAS hard drive for data backup
Optical drives (CD, DVD, HD-DVD, Blu-Ray)
Backup files located on the will be saved on a medium located in the optical drive. will be created automatically. Saved files are marked as “replicated to optical drive” and will not be saved again during the next replication (see: RepAttrib command).
Tape drives (streamers) and tape libraries (autoloaders)
Backup files located on the backup server will be saved on a medium (DDS, DLT, LTO, AIT, etc.) located in the tape drive. FBF subdirectories will be created automatically. Saved files are marked as "replicated to tape drive" and will not be saved again during the next replication (see: RepAttrib command). Before using a tape for backup replication it should be formatted in FBTF (Ferro Backup Tape Format) using the "Delete" command. FBTF files can be retrieved using the "Read file..." command.
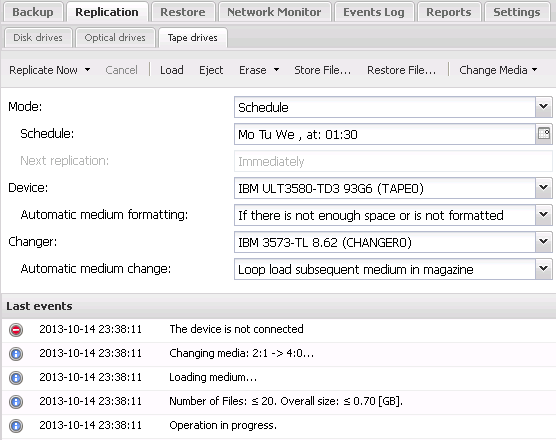
Fig. 2.2 FBS Server - Replication on a streamer with autoloader support.
Below, only options available for tape libraries and autoloaders are described.
- Change the drive (a command available only for tape libraries and autoloaders)
- From the socket to the drive - it enables to load a tape from a defined socket to the drive
- From the drive to the socket - it enables to load a tape from a defined drive to the socket
- Automatic medium formatting
- Disable - the program does not execute automatic tape formatting
- Always - before every replication - program formats the tape before every replication
- If there is not enough space or is not formatted - the program formats the tape when there is not enough space for replicated backup files or when the medium has not yet been formatted
- Automatic medium change (the option available only for tape libraries and autoloaders)
- Disable - the program does not execute automatic change of the medium in the drive
- Loop load subsequent media in storage - prior to every replication, a medium is loaded from subsequent socket. If the socket is empty, the program checks and loop loads tapes from subsequent sockets.
- Load medium from the socket for a given day of the week (0 - Mon, 1 - Tue, etc.) - prior to every replication, the program loads a tape to the medium from a socket corresponding to a given day of the week. It means that on Monday the tape from the first socket will be loaded, on Tuesday from the second socket and on Sunday from the seventh one.
- Load medium from the socket for a given day of the week (0 - 30) - prior to every replication, the program loads a tape to the medium from a socket corresponding to a given month.
See also: Data backup on tape drives (streamers), tape libraries and autoloaders
3. FBS Server - Data restore
In the Restore tab you can view backups and restore data from them. The Ferro Backup System makes it possible to perform full backup and differential backup. Nevertheless, whatever backup type you choose for your workstation, the data restore procedure is always carried out in the same, user-friendly way.
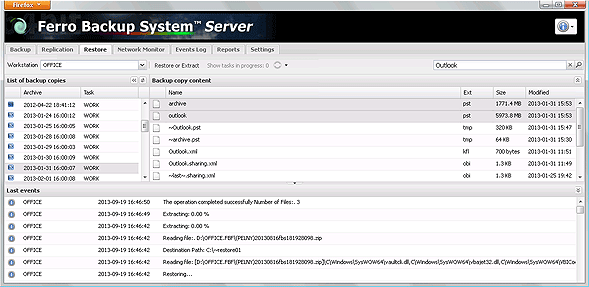
Fig. 3.1 FBS Server - Data restore.
- Workstation - a drop-down list where you can select the computer to view or unpack backup files from. The name of the workstation can be selected from the list or entered by typing. The list includes the names of computers which are defined in the System (they are displayed in the Backup tab) or were defined (have been removed and no longer appear in the Backup tab) but their FBF directory containing ZIP files are on the server. You can thus restore data from currently defined workstations and from workstations which are no longer connected to the System. After selecting a workstation a list of available backup files will be displayed in a field below.
- Backup files list - this shows a list of available backup files for a selected workstation. Each item specifies date and time of file creation. The number of items in this field corresponds to the number of backup files currently stored on the server. If no backups have been performed for a workstation, the field will be empty. Here you can choose, by selecting only one item, which data (from which day) is to be viewed or restored. It is thus possible to restore data not only from the last backup copy but also data from a specific date. After selecting an item from the list, a directory tree will appear in the right-hand window showing a list of backup files.
- Backup copy content - a list specifying file names, extensions, sizes and backup dates. After selecting a directory or a file, the Restore or Unpack button above becomes active. Please note that if a large number of differential backup files from your workstation are stored on the server, building a directory tree might take a while.
- Restore or unpack - use this to unpack (extract) selected files or directories from ZIP archives. In full tasks, only files from a selected full backup are restored. For differential tasks, the selected differential task is restored as well as all previous backup archives linked to it.
After clicking on Unpack a window will pop up in which you need to enter a destination path for the selected files or directories.
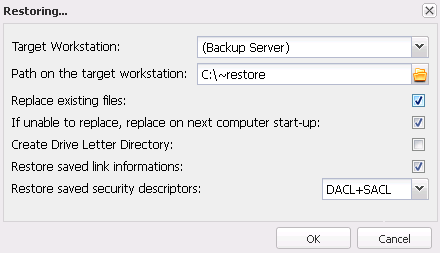
Fig. 3.2 FBS Server - Data restore - options
- Show tasks in progress - shows the number of active tasks to restore. The list of tasks to restore is displayed after clicking the button. After selecting a task, it is stopped.
- Search - use this to search for files and directories with a particular name in a selected backup task. In full tasks only a full backup is searched. For differential tasks, the selected differential backup is searched as well as all previous backups linked to it. Wildcards may be used for search.
See also:
Restoring operating system or entire disk partition from backup copy
4. FBS Server - Network monitor
The Network Monitor tab is used to monitor the operation of the backup server. It includes two information fields, buttons to stop and launch the TCP server and buttons to load a virtual command line on the backup server and workstations.
The Server Statistics window on the left-hand side displays the following information:
- Computer name (server) - NetBIOS or DNS of the computer on which the FBS Server is running (see: ).
- System version - name and number of the version of the operating system installed on the backup server
- IP address - Internet Protocol (IP) address of the computer on which the FBS Server is running
- TCP port - number of the TCP port on which the FBS Server awaits for the connections from workstations (usually 4531)
- Server version - the version number of the software of the FBS Server launched on the backup server
- Client version - the version number of the software of the FBS Worker, available on the backup server
- Launch - date and time of TCP server launch
- Status - current status of TCP server
- Active connections - number of connected with the . The number of connections in progress (when the server and a workstation are still negotiating a connection) can be displayed in brackets.
- Inactive connections - number of defined in the Backup tab which have not established connections with the .
- Licensee - name of the user entitled to use the program
- Maximum number of connections – the maximum number of remote computers that can connect to the server. Maximum number of connections depends on the purchased license (number of stations). In the evaluation version it is 2, which means that only 2 can connect to the . Exceeding the connection limit by installing the FBS Worker on more workstations than permitted in the license will shut down the TCP server.
- CPU - processor usage
- Memory - RAM usage (available/total, percentage of the available memory)
- Storage - storage disk space: free space, total size, percent of free space
- Download rate - displays the current rate at which data is being downloaded from workstations
- System uptime - a measure of the time the backup server has been working and available
 When you install the FBS Worker on workstations you need to state the name or address of the server. Those name and address details are displayed here (Computer name, IP address). When you install the FBS Worker on workstations you need to state the name or address of the server. Those name and address details are displayed here (Computer name, IP address).
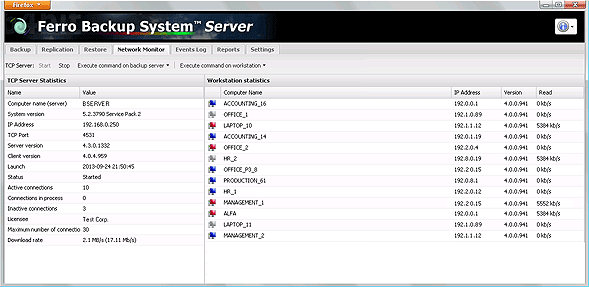
Fig. 4.1 FBS Server - Network monitor.
The window Active Workstations, located on the right-hand side, contains a list of workstations currently connected to the server and a handful of useful details such as:
- Name - NetBIOS or DNS of the
- IP address - Internet Protocol (IP)
- Version – version of the FBS Worker software installed on the .
- Read rate - displays the current rate at which data is being read from workstations
The following commands are available in the Network monitor tab:
- Start - Launching of the TCP server. The TCP server is launched and waits on port 4531 for incoming connections initiated automatically by the FBS Worker software installed on workstations. The Launch command is executed automatically when the FBS Server is run.
- Stop - this disconnects all workstations and shuts down the TCP server. This command is initiated automatically when the FBS Server software is stopped.
- Execute command on backup server - provides access to the virtual command line on the backup server. The Menu contains a list of most frequently used commands, including System Information, List of processes, Network Connections
- Execute command on workstation - provides access to the virtual command line on the workstation. The Menu contains a list of most frequently used commands, including System Information, List of processes, Network Connections
5. FBS Server - Event log
The Event log enables you to make sure the System is operating correctly and to search for the causes of any problems.
The Log tab makes it possible to systematically monitor all generated events pertaining to the operation of the whole System( the and ), such as errors, warnings and notifications. All recorded events can be filtered according to event type and computer name to which the notification referres.
The event list shows the following information:
- Event type (icon) – specifies the event type. Three types are available: error, warning, notification
- Station – name of the or component (marked with #)
- Time – date and time of event
- Task – backup task name (or empty)
- Event – event description (message)
- Operation - type of operation during which the event has been generated
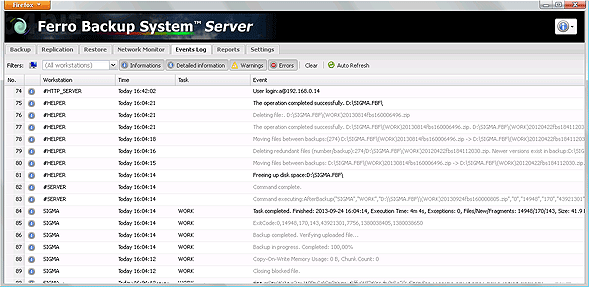
Fig. 5.1 FBS Server - Event Log.
 The event list can be filtered according to event type and computer name.
Events which do not meet the criteria defined in the filter(s) are not displayed. Regardless of filter settings, however, all events are always logged in the event log. The event list can be filtered according to event type and computer name.
Events which do not meet the criteria defined in the filter(s) are not displayed. Regardless of filter settings, however, all events are always logged in the event log.
Available commands (from left):
- Filter – changes filtering type
- Simple filter – for simple log filtering using controls (buttons, lists, check fields)
- Advanced filter – for advanced log filtering based on SQL (standard SQL-92). Only single SELECT queries are possible (including subqueries) on the LOG table. Field names are visible in the result grid header and real data are displayed when you hover the pointer over a cell.
SQL queries can also be used in administrative alerts "Event Log Entries". Example:
select name from
(select name, max(logtime) as updtime from log
where text = "#EC#2000006E" group by name) l1
left join
(select name, max(logtime) as contime from log
where text = "#EC#20000118" group by name) l2
on (l1.name = l2.name)
where updtime > contime
- Clear - clears the whole event history saved in the database. Events will be removed when the FBS Server is launched again. It is recommended to clear the event log regularly to increase system performance.
- Auto Refresh - if you turn this on, the event list will be scrolled automatically to the last logged event. Turning it off will enable you to view the whole history of logged events. If you do not analyze the contents of the event log, it is recommended to switch this off to reduce server load.
6. FBS Server - Reports
Reports enable the System's activities to be analysed quickly and easily. With reports it is no longer necessary to constantly monitor the System and analyze the Event Log. Reports are generated in HTML format and then uploaded to the Internet Explorer window in FBS Server. Using Administrative alerts, reports can be automatically generated and sent to a designated email address or FTP/web server.
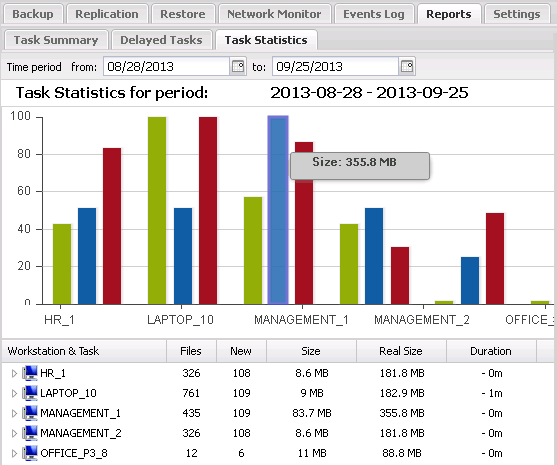
Fig. 6.1 FBS Server - Backup reports
Three types of reports are available. They are described in table 6.1.
|
Report name
|
Overview
|
|
Task Summary
|
Displays the following details for every workstation and every task: number of scheduled tasks, number of tasks completed successfully, number of tasks failed, percentage of successful tasks, number of tasks “in progress”, number of warnings, and status. For backup tasks which yielded errors or warnings, additional records are displayed showing error or warning details.
Only scheduled tasks – i.e. tasks which have been properly scheduled - are included in the report.
|
|
Delayed Tasks
|
Displays information about scheduled backup tasks which have not been completed. For each delayed task the process shows the length of the delay and the number of failed attempts. Additional records explain causes of failure. Only scheduled tasks – i.e. tasks which have been properly scheduled - are included in the report.
|
|
Task Statistics
|
This shows summary statistics for each workstation and each backup task and detailed statistics for a specified backup task. Each record shows the size of the completed backup archive, the number of files backed up, the number of new files in a differential archive, task duration and the average data transfer rate.
|
|
Storage Inventory
|
The report shows the use of space on backup server disks, divided into workstations, backup tasks and backup files. Each item may have information on the number of backups, the total size of backups on the disk and the date of the last backup. The graph shows free and used space on each storage disk.
|
You can set time intervals for each report. For example, in the "Delayed tasks" report you can choose to display only tasks which have not been completed for a specified number of days, weeks or months. In the "Task summary" and "Task statistics" reports you can define a time interval for data analysis.
7. FBS Server - Backup server settings
The Settings tab enables you to configure the basic settings for backup server, define archive encryption passwords, set administrative alerts, map network resources and create scripts to extend the program's functionality.
7A) Basic
- Main Backup Location – this field should specify the full path of the backup copy (ZIP files) location. If the specified directory does not exist, it will be created automatically on the first reference to that directory.
If the path is invalid (it points to a missing drive or contains invalid characters), an error message will be shown and the server will be stopped.
The directory will include for all .
The main backup storage location can be changed in the Workstation Settings window, setting a different path for each backup task (different hard disk or disk array).
 In order to ensure adequate performance, the backup storage directory should be located on a local hard disk or an internal disk array (RAID). Using network disks is not recommended. A network disk can be used as an additional storage location. For details see: Replication.. In order to ensure adequate performance, the backup storage directory should be located on a local hard disk or an internal disk array (RAID). Using network disks is not recommended. A network disk can be used as an additional storage location. For details see: Replication..
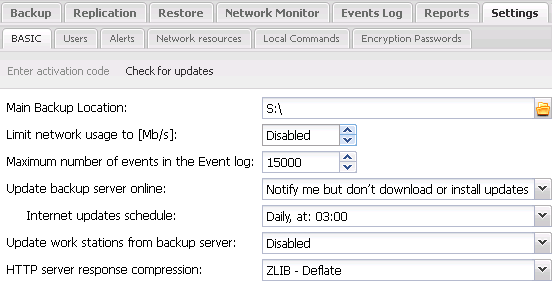
Fig. 7.1 FBS Server - Basic settings for backup server
- Limit network load - you can set the maximum computer network load here.
See also: Limit connection speed for a selected workstation
- Maximum number of Event Log entries - use this option to limit the amount of information stored in the Event Log and so reduce the FBS Server launch time.
- Update backup server online (see also: Program installation and update)
- Disable - deactivates backup server automatic updates
- Notify me but don't download updates - the program will, at a given time, check if a newer program version is available online. If a newer version is available, a warning will be recorded in the Event Log, stating that the installed version is not up to date.
- Automatically download and install updates - the program will, at a given time, check if a newer program version is available online. If a newer version is available, the program will automatically download and install the update. The program update process can be postponed if the program is performing other tasks or the user is working on the computer.
- Update work stations from backup server
- Disable - deactivates work stations automatic updates
- Enable - enables automatic software updates for work stations. The update is executed while connecting the work station to the backup server. After backup server (FBS Server) software installation (manual or automatic), the current work station software version (FBS Worker) is also stored on the server. The server sends a software copy to a work station while establishing a connection. The work station installs the new software version. While executing the update, the work station disconnects itself from the backup server for about 1 minute. The program update process can be postponed if the program is performing other tasks (backup).
- HTTP server response compression -turns on or off ZLIB-Deflate compression used by the HTTP server embedded in FBS Server. Enabling compression may increase the loading speed of the control console through an Internet browser.
- Allow HTTP connections only from these IP addresses - increases security by restricting remote access to the control console for the selected source IP addresses. If a connection originates from a different IP address, it will be rejected by the HTTP server.
Connections from the localhost are not blocked. The list may contain one IP address or multiple IP addresses, separated by commas.
- Verify archives periodically - when this option is enabled, it will check backups at specific intervals.
More information: Verify Archives command
- Disk write cache - this option allows to write back or write through the system cache for writing operations performed by the backup system.
Enabling the write cache may increase the backup and replication speed.
These options should be disabled in order to limit CPU and RAM usage.
- Two-Person Control Administration - this option allows to increase access security to backups and the most important administrative operations. The principle of operation is to limit access to restricted data by the necessity to authorize all operations
performed by the second operator (the so-called "two-man rule"). This option is useful in companies and institutions (e.g. banks, governmental institutions, army), where additional security procedures are required.
When this option is enabled, the following operations require authorization by the second administrator:
- Data recovery by the operator or administrator to the backup server.
- Data recovery by the operator or administrator to another workstation than the original one.
- Data recovery by the operator or administrator to the original workstation unless the user of this workstation is logged into the control console.
- Adding, changing and deleting user accounts
- Changing settings of the Two-Person Control Administration.
The operations can be authorized locally, in the same console where the operation was initiated, or remotely, in all the control consoles with administration rights.
Any operation that is not confirmed within 60 seconds is cancelled by the System.
- The title displayed in the browser - it defines the text displayed in a browser's title bar
- Enter activation code - displays a dialog that enables to enter the activation code to the licence key. When the correct key is entered, the program is registered and in the Network Monitor tab the licensee name and purchased number of hook ups will be displayed. If this option is inactive, it means that the program has already been registered.
- Check for the updates - FBS Server checks for the latest updates on the Internet. If an update is available, a new instruction will be displayed: Download and Install. When the update is finished, FBS Server will download a new version of the program on the backup server, then it will install it and restart FBS Server service.
See also: Automatic updates and program installation and update
- Verify Archives - this command checks whether the backup files stored on the backup server are correct. The result of this operation is recorded in the Event Log.
During backup, the FBS Server regularly checks backups sent by workstations. However, such verification is not able to detect some errors related to saving of the backups in storage.
Backup damages may result, among others, from failures and errors of hard drives, RAID arrays, file system, security programs. In order to verify whether the saved backups are correct, this command should be run at times
7B) Users
Here you can create user accounts for accessing FBS Server control console. If there is no account, the access to the console is not protected and everyone gets an administrator access.
- Account type - access account may have the following privileges:
- Administrator - an account with full privileges for control console
- Operator - an account with privileges for controlling data backup and restore but without privilege to change program settings
- Observer - an account with backup and restore process supervision but without privileges to control them or change program settings.
- Workstation user - an account with permissions to control backup and to recover data only for the workstation which the connection comes from. Logging in to this account is possible when:
- the name of the workstation is the same as the username
- the workstation is connected to the backup server
- the computer IP, which logging in to the console is made from, is the same as the workstation IP
- User - any username. The field is not case sensitive
- Password - access password. The field is case sensitive
- Comment - account description
- Add - creates a new account
- Modify - enables to change the settings
- Delete - removes selected item from the list
- Logout - ends current session. This command is also available in the menu located in the upper right corner of the screen
- Log everyone out - ends all sessions and releases HTTP server resources
7C) Administrative alerts
Administrative alerts are notifications including reports or chosen messages of the Event Log, which can be scheduled to be sent to designated email addresses, web servers (see: FTPUSE command) or syslog servers.
- Enabled - it means alert generating is on
- Name - any alert name. It is used as subject in an e-mail message
- Type - alert type
- Event Log entries
- Report Summary of tasks
- Report Delayed tasks
- Parameters - settings for chosen type of alert
- Schedule - how often the alert should be sent
- Next time limit - defines the time of the next alert to be sent
- Send empty - if this option is enabled, the alert is always sent at the same time. If this option is disabled, an alert is sent at a precise time only if it contains some data, e.g. for an alert Event Log entries with Error parameter, an alert will be sent only if since the last sending off, some events with Error status have been entered into the Event Log.
- Send to - email address, target directory (located, for example, on a web server) or syslog server address
- Add - creates new alert
- Modify - allows to change selected alert
- Delete - deletes selected alert
- Send now - a button to test current settings - test sending of alert
 Note. Semicolons (;) can be used to separate multiple message recipients, e.g. example@example.com; example2@example.com; ... Note. Semicolons (;) can be used to separate multiple message recipients, e.g. example@example.com; example2@example.com; ...
7D) Network Resources
In the Network Resources tab, define all UNC paths, mapped network disks and FTP server disks to be used by FBS Server in one of these locations:
It is necessary to configure network resources directly in FBS Server, because drives and network connections put together in various login sessions are not available for system services, such as FBS Server, which operate in separate sessions. Adding network resources is necessary only when a resource is available through SMB protocol (Samba/ Network environment). If iSCSI is used, defining network resources in the program is not needed.
See also: Using NAS hard drive for data backup
- Add - adds a new network resource to the list. The following types of network resources can be added:
- Mapped network disk - resource available in LAN, mapped to a local disk letter of backup server
- Mapped FTP serve share- FTP server resource mapped to a local disk letter of backup server
- Network share - network resource available through UNC path
- Modify - enables to change the settings
- Delete - removes selected network resource from the list
- Connect - connects the selected network resource
- Disconnect - disconnects the selected network resource
- Connection status - executes command NET USE on the backup server and returns a result in the virtual command line window.
Network resources are connected automatically when FBS Server is trying to access a given network resource - before backup, before replication, before sending an administrative alert or before opening a dialog for selecting the target directory. If a connection attempt is unsuccessful, the current operation that requires access to a given resource will be interrupted, and a relevant error will be entered in the Event Log. The minimum interval for reattempting to connect is 60 seconds. This limit is not used for manual connection (Connect button).
 A local system account on which the FBS Server is installed by default and does not have access privileges to network resources. Therefore it is necessary to switch the FBS Server service to an account which has such privileges (e.g. an administrator account) or to set relevant privileges for the Local system account. This can be done from the MMC Services console (Control panel->Administrative tools->Services).
A local system account on which the FBS Server is installed by default and does not have access privileges to network resources. Therefore it is necessary to switch the FBS Server service to an account which has such privileges (e.g. an administrator account) or to set relevant privileges for the Local system account. This can be done from the MMC Services console (Control panel->Administrative tools->Services).
7E) Local commands
Local commands allow to extend functionalities of FBS Server. They enable automatic running of external programs, scripts or input files, perform operations on files, use ActiveX components, control Active Directory services etc.
Local commands are built on the basis of FBS Server infrastructure Windows Script. FBS Server, like Windows Script Host (WSH) or Internet Explorer, is a script host independent from the language. Local Command scripts have access to Microsoft ActiveX (COM) components, Application Programming Interfaces (API) for Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and ADSI as well as additional functions integrated in FBS Server.
Available commands:
- New - deletes the current script
- A new script with event template - deletes the current script and loads a template for a selected language with definitions of all the events available
- Language - choose a script language
- Test - check the script syntax as a whole and run a procedure indicated in procedure launch edit field, on the right hand side. The code is executed on the backup server with account privileges on which FBS Worker runs.
- Stop - stop running the script
- Procedure launch edit field - used to provide the name of the procedure to be run (test run), along with all the parameters to be sent to the procedure. A syntax as per the script language chosen must be used in this field.
- Script to be executed on backup server - space for script code. The Local Commands code can be written in any (previously selected) script language installed in the operating system on the backup server. By default, two Active Script engines are available in Windows: JScript and VBScript. To use other script languages, first install an engine for a given language in the operating system. The most commonly used script languages are: JScript, VBScript, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, Object Pascal, Forth, Haskell, TCL.
Events
Local Commands use an events mechanism. FBS Server generates events in a given program operating status and runs a procedure to handle this event as defined by the administrator in Local Commands. For example: “BeforeBackup” event is generated before backup and control is transferred to “BeforeBackup” procedure. If the procedure to handle an event has not been defined, FBS Server will not generate the event.
A procedure to handle an event is a code fragment (procedure or function) defined in the chosen script language. Sample procedures to handle “BeforeBackup” event:
function BeforeBackup(Comp, Task, File) {
if (Comp == 'SERVER_BB')
SScript.Echo('Task name:' + Task);
}
All the available events along with declarations of procedures to handle events and parameters are described below in detail.
- OnStart
An event generated when starting the program
- OnStop
- An event generated when shutting the program
- Declaration
OnStop(AppType)
- Parameters
AppType - a number that specifies the program running mode. This parameter may have the following values.
- 0 – system service
- 1 – user application
- BeforeBackup
An event generated before backup
- AfterBackup
An event generated after backup
- Declaration
AfterBackup(Comp, Task, File, Error, Files, NewFiles, ArchiveSize, UncompressedSize)
- Parameters
Comp - a string of characters that specifies the computer name
Task - a string of characters that specifies the backup task name
File - a string of characters that specifies the path and target file name (ZIP archive)
Error - a number that specifies the backup result. This parameter may have the following values.
- 0 – backup successfully completed
- different than 0 – backup error
Files - number of files in the backup
NewFiles - number of new or modified files in the backup. If the value of this parameter is equal to Files parameter value, it means that this copy is a full copy.
ArchiveSize - ZIP file size
UncompressedSize - overall size of all the files in the backup after decompression
- Example
Saving the list of files contained in a backup copy (ZIP archive) when using 7-Zip. 7-Zip is run from the command shell (CMD) to forward the standard output stream from the screen to the file.
function AfterBackup(Comp, Task, File, Error, Files, NewFiles,
ArchiveSize, UncompressedSize) {
if (Error == 0)
SScript.Run('cmd /c 7z l "' + File +'" >"' + File + '.txt"');
if (Files == NewFiles)
SScript.Echo('Full backup exectuted');
else
SScript.Echo('Differential backup executed');
}
- BeforeReplication
An event generated before replication
- Declaration
BeforeReplication(Comp, Task, RepType, DestPath)
- Parameters
- Comp – a string of characters that specifies the computer name. An empty string means a replication for all computers
Task - a string of characters that specifies the backup task name. An empty string means a replication of all backup tasks for a given computer
RepType - a number that specifies the replication type. This parameter may have the following values.
- 1 – replication into a disc medium
- 2 - replication into an optical medium
- 3 - replication into a tape medium
DestPath - a string of characters that specifies the access path to the target directory (1) or the device name (2,3)
- Example
Change a medium in a tape drive using RSM command
function BeforeReplication(Comp, Task, RepType, DestPath) {
if (RepType == 3) //MTD
SScript.Run('RSM MOUNT ' +
'/PF"MEDIA_NAME" /CF"CHANGER_NAME" /OREADWRITE');
}
- AfterReplication
An event generated after replication
- Declaration
AfterReplication(Comp, Task, RepType, DestPath)
- Parameters
Comp – a string of characters that specifies the computer name. An empty string means a replication for all computers
Task - a string of characters that specifies the backup task name. An empty string means a replication of all backup tasks for a given computer
RepType - a number that specifies the replication type. This parameter may have the following values.
- 1 – replication into a disc medium
- 2 - replication into an optical medium
- 3 - replication into a tape medium
DestPath - a string of characters that specifies the access path to the target directory (1) or the device name (2,3)
- Example
Eject medium from a tape medium using RSM command
function AfterReplication(Comp, Task, RepType, DestPath) {
if (RepType == 3) //MTD
SScript.Run('RSM eject /pf"MEDIA_NAME" /astart');
}
- OnReplicationError
An event generated after an error has occurred during replication
- Declaration
OnReplicationError(Comp, Task, RepType, DestPath, Error)
- Parameters
Comp – a string of characters that specifies the computer name. An empty string means a replication for all computers
Task - a string of characters that specifies the backup task name. An empty string means a replication of all backup tasks for a given computer
RepType - a number that specifies the replication type. This parameter may have the following values.
- 1 – replication into a disc medium
- 2 - replication into an optical medium
- 3 - replication into a tape medium
DestPath - a string of characters that specifies the access path to the target directory (1) or the device name (2,3) This parameter can have values of system error codes.
Example:
- 11 - (ERROR_BAD_FORMAT) a medium has not been formatted
- 1100 - (ERROR_END_OF_MEDIA) no space on the medium
- 1112 - (ERROR_NO_MEDIA_IN_DRIVE) no medium in drive
A full list of error codes for Windows is available on page: System Error Codes
- Overview
If an error has been handled, the true (1) value must be returned. In that case, the last replication will be retried. If the same error occurs when the operation is retried, replication will be interrupted (OnReplicationError event will not be generated again). If the false (0) value is returned, replication will be interrupted.
- Example
Format the tape if it has not been formatted or if it is full
function OnReplicationError(Comp, Task, RepType, DestPath, Error) {
if (Error == 11 | Error == 1100) { //BAD FORMAT or END OF MEDIA
SScript.TapeFormat(false, 'NEW_TAPE_NAME');
return true;
}
}
FBS Server (or more precisely: a thread that generated the event) is suspended until the script operation is completed. Script running duration is limited by default to 3 minutes. When this limit is exceeded, the script is interrupted and FBS Server is resumed. (The running time limit can be redefined within the script using SScript's Timeout property)
SScript (server script) is an object integrated in FBS Server. It is a global object, created automatically, available from any location within the script.
SScript is an equivalent of WScript integrated in Windows Script Host. It provides access to several useful methods and properties which are described in detail below.
- Echo
The method saves a given text in the Event Log
- Definition
Echo(EventText)
- Parameters
EventText - a string of characters to specify an event text
- Example
Information is saved in the Event Log
SScript.Echo('Text');
- Log
The method saves a given text in the Event Log and marks the entry as information, warning or error
- Definition
Log(EventType, EventText)
- Parameters
EventType – a number to specify the event type. This parameter may have the following values.
- 0 - information
- 1 - warning
- 2 - error
EventText - a string of characters to specify an event text
- Example
Information is saved in the Event Log
SScript.Log(1, 'Text');
- TapeFormat
The method formats a tape medium in FBTF
- Sleep
It suspends script operation for a given time
- Definition
Sleep(intTime)
- Parameters
intTime – an Integer number to specify a period expressed in milliseconds during which a script is to be suspended.
- Example
Script operation suspended for two seconds
SScript.Sleep(2000);
- Run
It runs a given program
- Timeout
It specifies the maximum script completion time
- StdOut
It returns the contents of a standard output stream
Additional automation objects
SScript is the only object integrated in FBS Server. However, any automation objects (OLE) can be used in Remote Commands. Access to other objects is made available in a manner specific to each script language.
By example, for JScript language, you need to call ActiveXObject; for VBScript - CreateObject. Here follows a list of the most common used automation objects.
- FileSystemObject
A group of objects for managing discs, directories and files
- Automation server name: Scripting
- Class name: FileSystemObject
- WshShell
An object used to run programs, manage the system register, create shortcuts, etc.
- Automation server name: WScript
- Class name: Shell
- WshNetwork
An object used to map network discs and printers, connect network resources and to read the computer name, domain name and user name
- Automation server name: WScript
- Class name: Network
Useful information:
See also: Remote Commands
7F) Encryption passwords
Here, you can enter passwords, used by the System to encrypt data during backup and decrypts them during data restore. If no password is defined, backup is not encrypted even if in an Encryption algorithm for the settings of backup has been chosen.
- Type of password - this field can contain the following:
- Encryption and decryption - password is to encrypt and decrypt backup files
- Decryption - password is to decrypt backup files only
- Password - password to encrypt or decrypt backup The fields are case sensitive
- Creation date - date of entering the password on the list
- Comment - any entry
- Add - creates a new password
- Delete - removes selected item from the list
 Note. Deleting a password used to encrypt an archive will make subsequent restoration of information from that archive impossible. Note. Deleting a password used to encrypt an archive will make subsequent restoration of information from that archive impossible.
- Set as current encryption password - changes the allocation of the password from decrypting to encrypting and decrypting
Multiple decryption passwords and one encryption/decryption password can be defined.
See also: Workstation settings - File encryption method
8. FBS Server - startup, stop and diagnostics
The FBS Server can be launched as a system service or , in an emergency, in user application mode.
8A) Program startup in the system service mode
Working as a system service is the main operating mode configured for automatic execution of backup of FBS Server. The service is launched automatically at the system startup.
Manual launching and stopping of FBS Server can be executed by:
- MMC service console (Control panel -> Administrative tools > Services -> FBS Server)
- commands such as NET START, NET STOP with FBSServer, such as NET START FBSSERVER
- running the FBSServer.exe with a parameter /START or /STOP, e.g. FBSServer /START
Once started, the service works in the background, by default, on a local system account. FBS Server control console is available by an Internet browser.
If there are any problems running the service or the service shuts down, read: Launching program in the diagnostics mode.
8B) Launching program in the diagnostics mode
If there are any problems running the FBS Server service or the service shuts down, launch program in the diagnostics mode. To do that, on the backup server, run the command line, go to the directory where the device is installed and write the following command:
FBSServer /debug
If the program launches correctly in diagnostic mode, you should load control console and then, go to the Events Log and diagnose the problem with launching services, by searching for the last errors reported by the program.
If the program does not launch in diagnostic mode and reports an error related to the database, launch a program with a parameter / repairdb, in order to repair a damaged database:
FBSServer /repairdb
FBSServer /repairdb
If the operation of repairing database fails or the program running in diagnostic mode reports another error, contact technical support.
8C) Solving control console access problems
If an Internet browser cannot load the control console page, do the following:
If all the above mentioned testing steps have successfully been executed and still there is no connection with the control console, please contact the technical support.
9. FBS Server - syntax and command shell parameters
Syntax:
FBSServer [/install | /uninstall] | [/start | /stop] | /repairdb | /debug
Parameters:
without parameters
shows this message
/install
installs FBS Server as a system service (automatic startup, SYSTEM account)
/uninstall
uninstalls FBS Server service
/start
runs the FBSServer service
/stop
stops the FBSServer service
/repairdb
repairs program database corruptions
/debug
starts the program in the diagnostics mode
/gui
opens a control console
User manual for the Ferro Backup System™ - Worker
FBS Worker is a small program (140 kB) which, when requested by the server, makes backups of files, folders or entire drives and sends the resulting backup copy to the server. The backed-up information may be compressed and encrypted. The compression process is carried out “on the fly” while the file is being sent (no temp files are created), which is why backups can be performed even when there is not enough space on the workstation’s disk. The encryption process is also performed locally on the workstation, which significantly improves the security of transmitted information.
FBS Worker is ready to use right after installation. The program is launched automatically during system startup. No additional configuration is needed. The remaining information in this text is for IT specialists only.
|
|
1. FBS Worker - description of available configuration file options
|
See below for a sample configuration file FBSWorker.ini, which the program uses to load its settings during startup. Changing default settings is not required to ensure correct System operation.
;FERRO Software Ferro Backup System - Worker
;Config file
;02-02-2007
[CONNECTION]
;Description: name or IP address of a computer running FBS Server
;Comments: empty string means the host name is assigned to a localhost (127.0.0.1)
HOST=192.168.0.2,SECONDARY_BACKUP_SERVER
;Description: TCP port, used to connect to the server
;Range: 1 - -65535
;Default: 4531
;Comments: currently this must be set to 4531.
PORT=4531
;Description: interval between subsequent server reconnect attempts
;Unit: millsecond [ms], Range: 0 (no delay) - 16777216
;Default: 4000
RECONNECTINTERVAL=4000
[COMPRESSION]
;Description: Max number of compression threads
;Range: 1-32
;Default: Empty string = Number of processors + 2
THREADSMAX=
In order to change the settings, open the FBSWorker.ini file in any text editor (Notepad, WordPad), and then save it as text. Changes made will only take effect after the program is launched again.
- CONNECTION - HOST
This is where the name/IP address of the backup server is stored (of the computer on which the FBS Server is launched), as entered by the user during program installation.
If during the use of the System the FBS Server is moved to another computer or if that computer’s name or IP address changes, the user can change the server location in this field to the correct one.
Changing this field manually will have the same effect as launching the installer and reentering the name/IP address during the installation of the FBS Worker.
Optionally, you can provide the name or IP address of a secondary backup server separated by comma.
- CONNECTION - PORT
Number of the TCP port used to connect to the server.
- CONNECTION - VIRTUALNAME
Alternative name of the computer under which it will be available on the backup server. FBSServer uses names (rather than IP addresses) to identify . If the local network is divided into two or more subnetworks with duplicate workstation names, only one workstation will be connected to the backup server; no subsequent workstations of the same name will be available in the FBS Server control console. In order to resolve this issue change the default name on computers with duplicate names: VIRTUALNAME=NEW_NAME
 Information. The computer name should not be longer than 15 characters. Information. The computer name should not be longer than 15 characters.
Other FBS Worker module settings can be configured remotely from the FBS Server console ( tab Workstation settings)
|
|
2. FBS Worker - startup
|
The FBSWorker.exe can be launched as a system service or user application.
System service
Working as a system service is the main operating mode configured for automatic FBS system backup.
The FBSWorker service can be launched and stopped by:
- going to the Services console (Control panel -> Administrative tools -> Services)
- running NET START, NET STOP commands using the FBSWorker parameter
- running the FBSWorker.exe using the /START or /STOP parameter
Once started, the service works in the background, by default on a local system account. If there are any problems running the service or the service shuts down, launch the FBSServer as an application and view the system Event Log.
Application mode
When run as an application, the program functions exactly the same as in system service mode, but is stopped when the user logs out of the system. In addition, if the program is working in this mode, the following text will be displayed in the FBSServer console: "FBS Worker operating in the emergency mode”.
To run the program as an application, run FBSWorker.exe directly without any parameters.
|
|
3. FBS Worker - syntax and command shell parameters
|
Syntax:
FBSWorker
FBSWorker [-install [/hostname:BackupServer]]
FBSWorker [-uninstall [/hostname:]]
FBSWorker [-start]
FBSWorker [-stop]
FBSWorker [-recovery BackupServer [LocalIPAddress SubnetMask [DefaultGateway]]]
Parameters:
without parameters
Runs the FBSWorker in the user application mode (emergency mode)
-install [/hostname:BackupServer]
Installs the FBSWorker as a system service (automatic startup,
SYSTEM account). If used with /hostname swith a configuration file
(FBSWorker.ini) will be created, which will contain the name or IP address
of the backup server
-uninstall [/hostname:]
Uninstalls the FBSWorker service. If used with /hostname swith followed by
an empty string (space) after the colon will delete the configuration file
(FBSWorker.ini) from the disk
-start
Runs the FBSWorker service
-stop
Stops the FBSWorker service
-recovery BackupServer [LocalIPAddress SubnetMask [DefaultGateway]]
Runs the FBSWorker in the recovery mode
/? Displays help at the command prompt
Remarks:
BackupServer : Specifies the destination backup server, which is identified
either by IP address or host name.
LocalIPAddress : Specifies the local address to configure
SubnetMask : Specifies the subnet mask for the IP address being configured
DefaultGateway : Specifies the IP address of the default gateway
to be configured
Examples:
FBSWorker
FBSWorker -install
FBSWorker -install /hostname:192.168.100.100
FBSWorker -uninstall
FBSWorker -uninstall /hostname:
FBSWorker -start
FBSWorker -stop
FBSWorker -recovery 192.168.100.100
FBSWorker -recovery 192.168.100.100 192.168.111.112 255.255.255.0
FBSWorker -recovery 192.168.100.100 192.168.111.112 255.255.255.0 192.168.100.1
|
|
4. FBS Worker - Solving connection problems
|
The FBS Worker application is launched automatically upon system startup and, at selected intervals (the RECONNECTINTERVAL option), attempts to reconnect to the selected computer (the HOST option) using the TCP 4531 port. When the connection is established, the computer’s name and IP address are displayed on the list of active workstations in the FBS Server program in the Network Monitor tab.
If the FBS Worker fails to connect to the server:
- check if the FBS Worker is running in the Windows task manager (the FBSWorker.exe process)
- check that the HOST entry is correct in the FBSWorker.ini file
- check (for example using the PING command) that the computer on which the FBS Server is installed is available
- check that the TCP 4531 port is not blocked by any firewall software.
In order to diagnose why there is no connection between the workstation and the backup server, you can use the TCPCHK program available in the Download section.
|
See also:
|
|













 No connection
No connection
 Ready to work
Ready to work
 Task preparation on server side
Task preparation on server side
 Task running
Task running
 Software update
Software update
 Workstation disabled
Workstation disabled
 Stopped
Stopped
 Running
Running


